Swift GCS Overview
Lynx VTOL is an autonomous unmanned aircraft (drone) and capable of performing a mission from takeoff to landing without any intervention. It is highly advised that you still monitor the aircraft during the entire flight. The GCS receives live updates regarding the aircraft through the telemetry radio. You may change flight modes or intervene with the mission while flying. Uploading a new mission(s) or modifying an existing mission in flight is also possible.
The GCS is comprised of the following distinct sections.
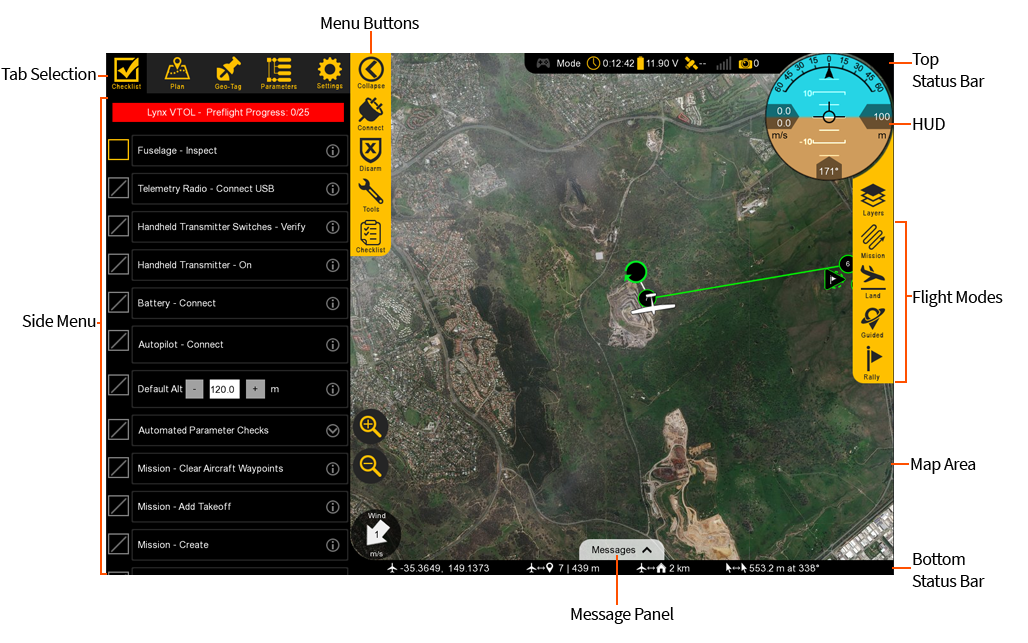
Tab Selection
Used to select which tab you are on, each with a particular function. There are five tabs: Checklist, Plan, Geo-Tag, Parameters, and Settings.
Checklist: The Checklist tab is used to perform a preflight on your Lynx VTOL prior to every takeoff.
Plan: The Plan tab is used add waypoints, survey grids, actions, or rally points to your mission. The Plan tab is utilized during the preflight process but can also be used to modify a mission in flight.
Geo-Tag: The Geo-Tag menu is used to geo-reference images for mapping applications that do not require high accuracy. For post-processed kinematics (PPK) tagging, the standalone GeoTagz software is used. Geotagz is included with Lynx VTOL with the PPK option.
Parameters: The Parameters Tab is an used to modify and update parameters on the autopilot. Parameters are only to be changed if instructed to do so by SRP Aero support.
Settings: The Settings tab is used to configure GCS, equipment, and autopilot settings. The settings tab is also used to update firmware and license keys.
Side Menu
The side menu corresponds to what tab you are on.
Menu Buttons
Each menu has unique buttons that change depending on which tab you are on. The very top button is used to collapse or expand the entire side menu. This can be useful when you are flying as it increases the overall map area.
Top Status Bar
Displays important aircraft information.
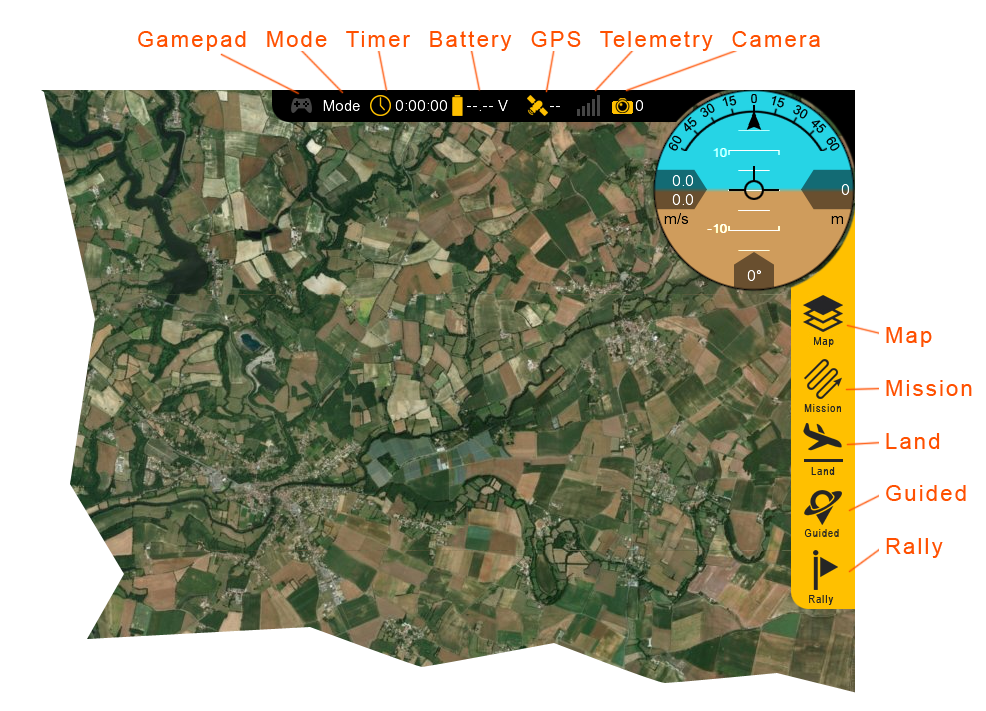
Gamepad: Indicates if a gamepad is connected to Swift GCS. This connection may be USB or Bluetooth. Swift GCS only recognizes XBox controllers. Note, this functionality is not fully supported at this time.
Mode: Displays the current flight mode.
Timer: Displays the current flight in Hours:Minutes:Seconds. The timer automatically starts on takeoff and stops when the aircraft lands and disarms. The aircraft must be restarted (turned off and on) to reset the timer.
Battery: Displays the main battery voltage. Click on the battery icon to expand this menu. The VTOL battery voltage is displayed in the expanded menu.
Telemetry: Displays the telemetry radio’s signal strength.
Camera: The camera icon displays photo count for cameras equipped with feedback. Feedback is essential for PPK tagging but is also helpful to see if and when the camera is taking photos.
Flight Modes
Used to change modes and aircraft location.
Map: The Map menu is used to configure how the aircraft icon and waypoints are displayed on the map. Under this menu is also where you can toggle the terrain view and load KML overlays.
Mission: In the mission menu, you can change the flight mode to Auto, restart the mission, or select an individual item in your mission to fly to.
Land: Select land to begin your planned landing or to execute an emergency landing.
Guided: The Guided flight mode is a 'fly here' mode. In Guided, you choose a spot on the map that the aircraft flies to and circles.
Rally: The Rally flight mode is automatically used when the aircraft completes its mission or a failsafe activates. You can also select the Rally flight mode. In this flight mode, the aircraft will navigate to the nearest Rally point and circle.
Bottom Status Bar
Displays aircraft location and waypoint information.
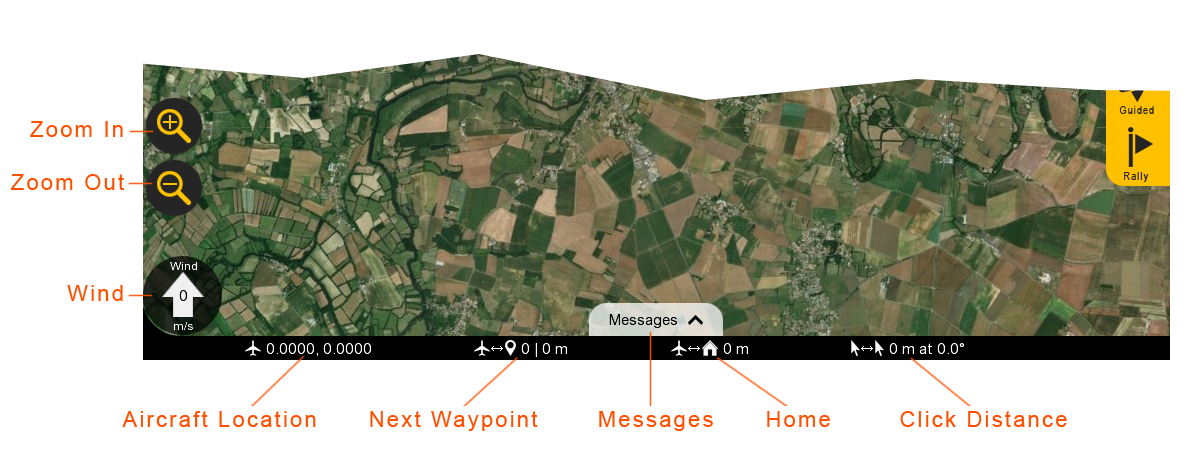
Zoom in/Out: Zooms the map area in or out. On touchscreen devices, you can also use ‘pinch-zoom’.
Wind: Displays the wind velocity and direction that the wind is blowing.
Aircraft Location: Current aircraft location coordinates shown in decimal degrees format.
Next Waypoint: Displays the next waypoint number in your mission and the distance to that waypoint from the aircraft.
Messages: The message panel displays warnings and notifications from the GCS and autopilot. A new warning will automatically expand the message panel if it was collapsed.
Home: Shows the distance from the aircraft to home. If you have a tablet with built-in GPS, this can be toggled to show the distance from the aircraft to your location.
Click Distance: Click distance shows the distance between your last two mouse clicks. This is a quick and useful tool for planning purposes such as determining how far away something is on the map.
HUD
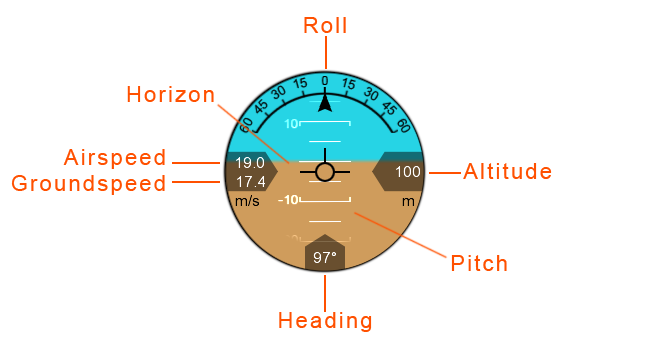
The Heads-Up Display (HUD) displays aircraft information and attitude against a horizon line.
Roll: The aircraft’s roll in degrees (bank angle).
Altitude: The aircraft’s altitude above the ground. The unit is displayed below the altitude reading.
Pitch: The aircraft’s pitch in degrees.
Heading: The aircraft’s magnetic heading.
Horizon: The aircraft’s attitude is shown against an artificial horizon.
Ground Speed: The speed of the aircraft relative to the ground. The unit for both ground and airspeed is displayed below.
Ground speed is affected by wind.
Airspeed: The speed of the aircraft relative to the air through which it is moving.
Airspeed is not affected by wind and should remain relatively constant in straight and level flight. Climbs or descents may have an affect.
Map Area
The Map displays the background satellite imagery with the position of aircraft flying over it. Currently there are two sources of map imagery: Mapbox and ESRI. The map area is also where your mission items and polygons will be shown.
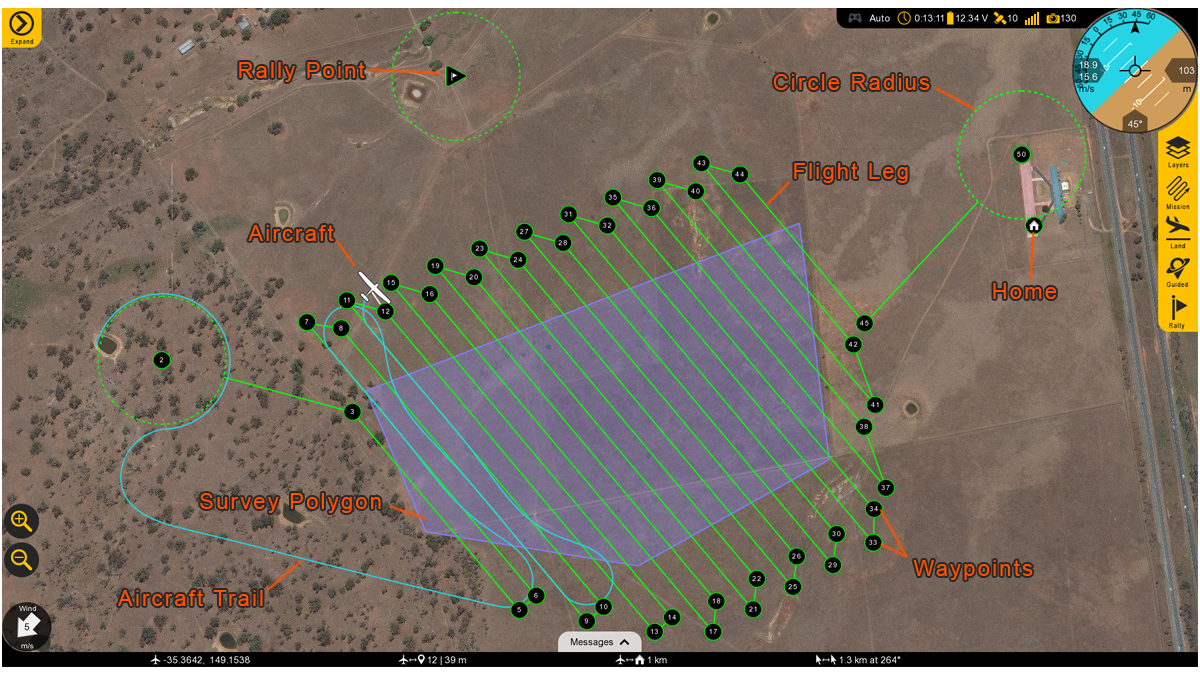
Rally Point: The Rally icon shows the location of your planned Rally points. The icon is a flag within a triangle.
Flight Leg: The flight legs connect each waypoint in sequence. They are an approximate indication of how the aircraft will fly from one waypoint to the next. They do no account for the turning radius of the aircraft. It is normal to observe small deviations from the flight legs in windy conditions.
Circle Radius: A dashed line will appear around certain waypoints that have a radius. Examples include the landing pattern and loiters.
Home: Displays the home location. Home is your takeoff location.
Waypoints: Displays the location of your planned waypoints. Each waypoint is numbered. Waypoints are used to fly to a location in the sky. The aircraft will fly through or near the waypoint and then proceed to the next item in your mission. Waypoints are automatically generated when creating a survey.
Survey Polygon: A survey polygon displays the area on the ground that you are mapping. Survey polygons are created from the
Plantab ⇨Survey. You can draw a new region or load a KML or KMZ (Google Earth format). Flight legs will extend past the polygon area to account for the extra space that the aircraft needs to turn around. Viewing the polygon can be toggled on/off from theMapbutton ⇨Survey. Multiple survey areas can be planned into your mission.Aircraft Trail: The aircraft trail shows the history of the aircraft’s flight path. At a certain length, the trail will automatically begin to disappear. The trail can also be clear manually from the
Mapbutton ⇨Clear Aircraft Trail.Aircraft: Displays the aircraft location and heading.